KUMASI, Dec 31 (Futball Surgery)- Investigations into South Korea’s plane crash on Sunday have intensified as on Tuesday, airport authorities have come under pressure imposed by families of dead to explain how the plane lost control and to identify victims.
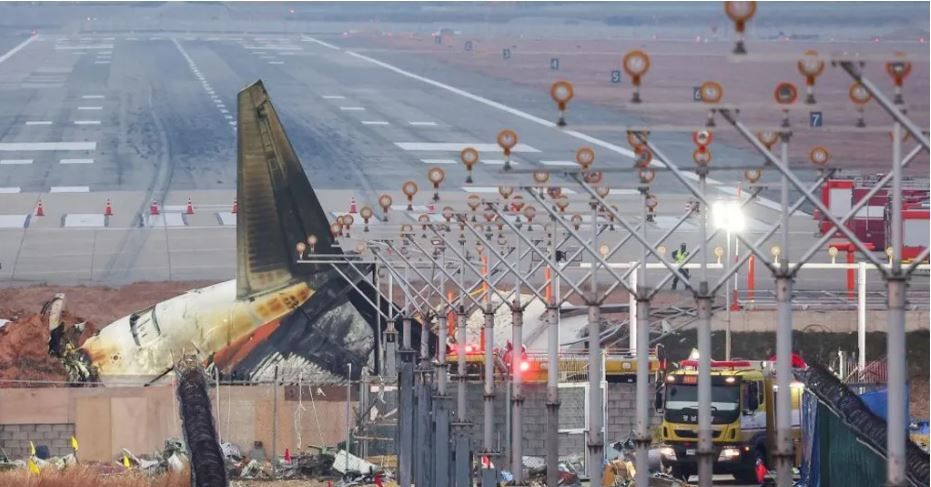
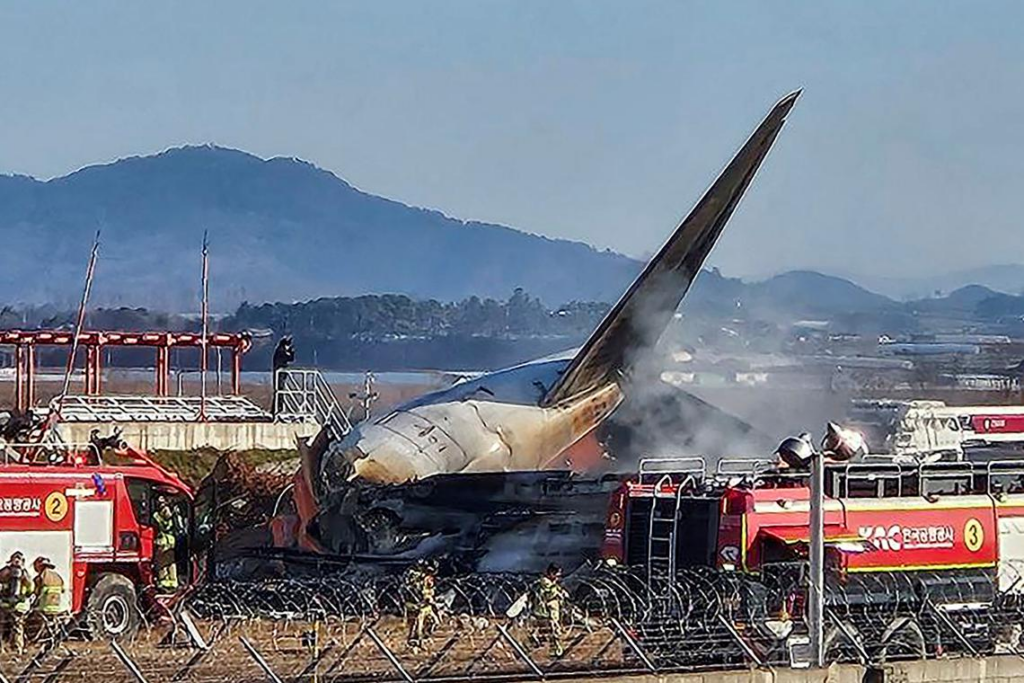
The plane, one of Jeju Airlines arriving from Bangkok hit a wall at the Muan International Airport before taking emergency landing and burst into flames.
All but two of the 181 people onboard are reportedly dead, according various source in Europe and Asia, which the incident is one of South Korea’s worst civil aviation disasters in history.
To speed up the process of identification of bodies has the National Police Agency of South Korea said it had enlisted additional officials and would use rapid DNA analysers to identify five bodies. All of the other victims have been identified but most remain at a temporary morgue at the airport, The Guardian reports.
Some of the in-the-process-investigations findings are suggesting that passenger died from the accident because they were thrown out of the Jeju Air flight 7C2216 into the surrounding fields supposedly built with concrete- which does not meet aviation practice standards.
Air safety expert David Learmount told BBC that, had the “obstruction” not been there, the plane “would have come to rest with most – possibly all – those on board still alive”.
As investigations intensify, which one of the enquiries’ focal point has been the cause of the plane crash, early theory of a bid strike appears not the only main cause and this causation is somehow gradually being relegated to the background for a potential airspace-related problems.
Although some experts do not believe a collision of that kind – a relatively common occurrence in aviation – would have been forceful enough to prevent the pilot from lowering the Boeing 737-800’s landing gear as it approached the runway.
Aside the bird strike theory, investigators according to the Guardian are trying to establish if any of the aircraft’s control systems were disabled, as well as why the pilot apparently attempted to land so soon after declaring an emergency. The plane, powered by two CFM 56-7B26 engines, appeared to be travelling at great speed when the pilot attempted a “belly landing.”
“I can’t think of any reason for being forced to make a landing like this,” said aviation safety expert John Nance, a former military and commercial pilot who flew 737s for Alaska Airlines.
Criticism was mounting of the airport’s layout, with aviation experts questioning why a large dirt-and-concrete embankment used to support navigation equipment had been built about 250m from the end of the runway.
South Korean officials said the embankment was built according to industry standards, adding that airports in other countries had similar features.
But some experts questioned the need to build it so close to the end of the runway.
The runway design did not meet industry best practices, which preclude any hard structure like a berm – a raised bank – within at least 300m of the runway’s end, claimed John Cox, chief executive of Safety Operating Systems and a former 737 pilot.
The crash poses a serious challenge to South Korea’s new acting president, Choi Sang-mok, who has ordered an emergency safety inspection of the county’s entire airline operation, while the transport ministry will inspect all 101 Boeing 737-800s currently in operation in the country by the end of the week.
Choi, who replaced the impeached former president Han Duck-soo at the weekend, said the priority was to identify the remaining victims and support the passengers’ families. “Even before the final results are out, we ask that officials transparently disclose the accident investigation process and promptly inform the bereaved families,” he said at a disaster management meeting.
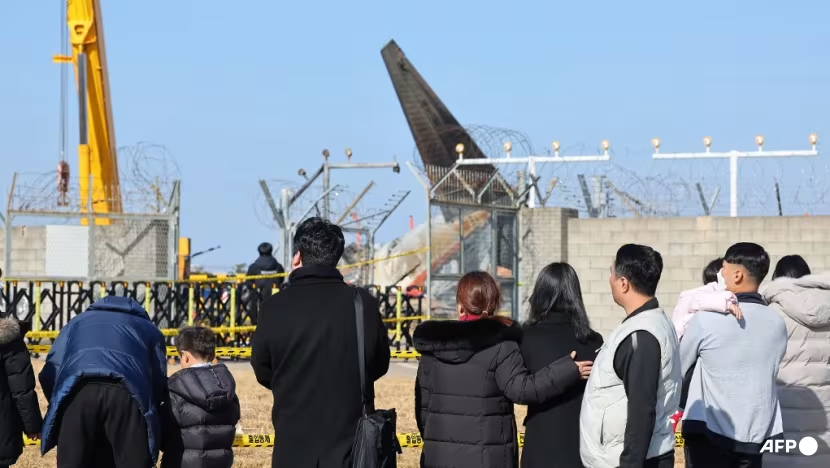
Choi immediately declared a seven-day period of mourning and paid his respect at a memorial at the crash site. Similar memorials have been set up at other locations around the country, and flags were flying at half mast.
Representatives from the US National Transportation Safety Board, Federal Aviation Administration, and aircraft manufacturer Boeing have joined the investigative body and planned to meet in Muan, 300 km south-west of Seoul, on Tuesday.
Establishing the cause of the accident could prove more complicated and time-consuming than usual, after the ministry said the plane’s damaged flight data recorder was missing key pieces, making it more difficult to extract its data. The second “black box” containing the cockpit voice recorder was in better condition, the Yonhap news agency said.
Park Han-shin, whose brother died in the crash, said he had been told by authorities that his brother had been identified but added he had not been able to see his body.
South Korean authorities will be under pressure to avoid a repeat of the aftermath of the Sewol ferry disaster in April 2014, in which more than 300 people, mostly high school students, died. Many relatives of the victims complained it took authorities too long to identify the dead and to establish the cause of the accident.
The bodies of four of the identified victims in Sunday’s crash have been handed over to their families, Yonhap said, citing local officials.